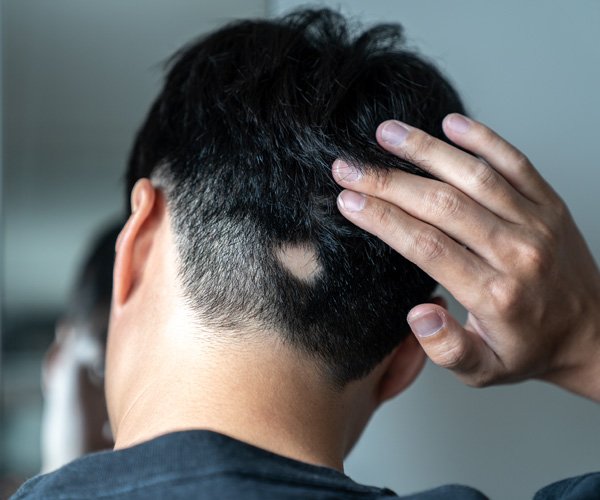
Understanding Alopecia Areata: Patchy Hair Loss Insights and Management Strategies
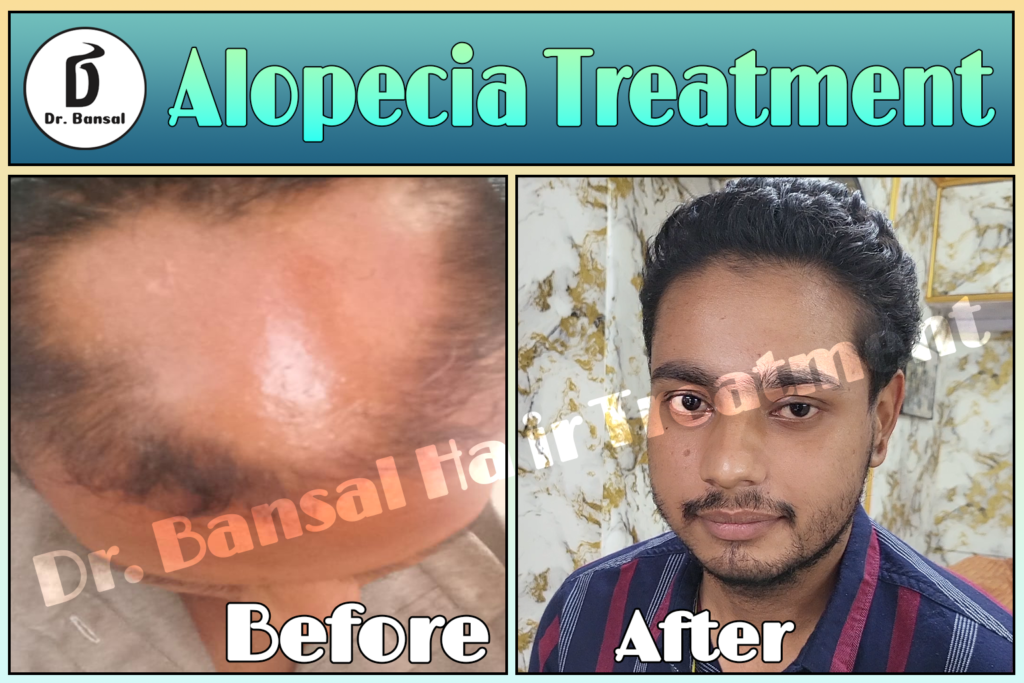
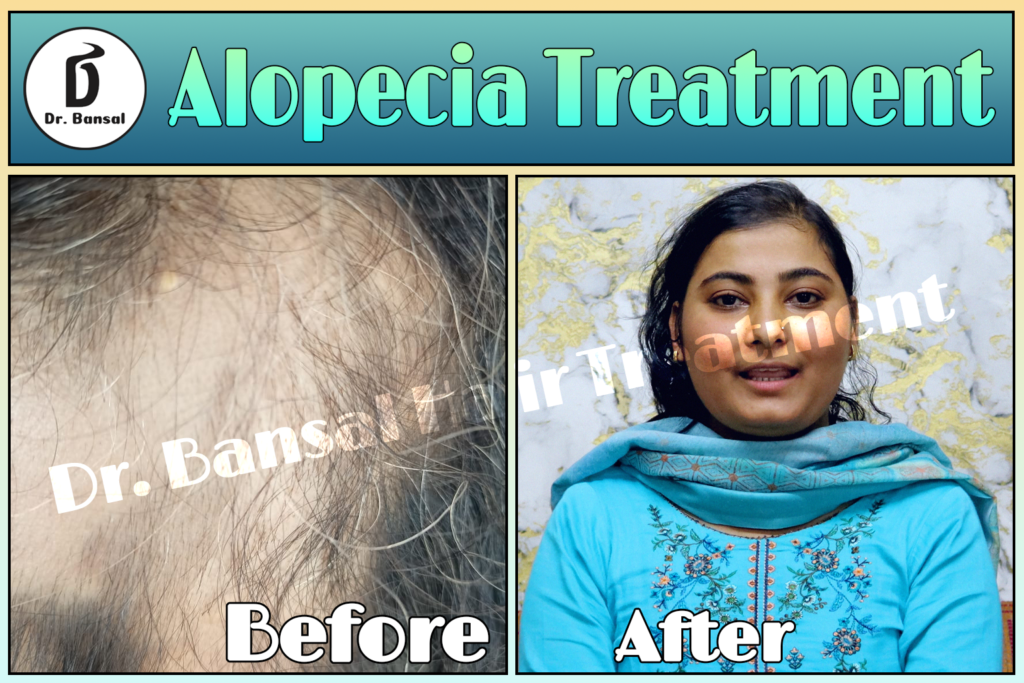
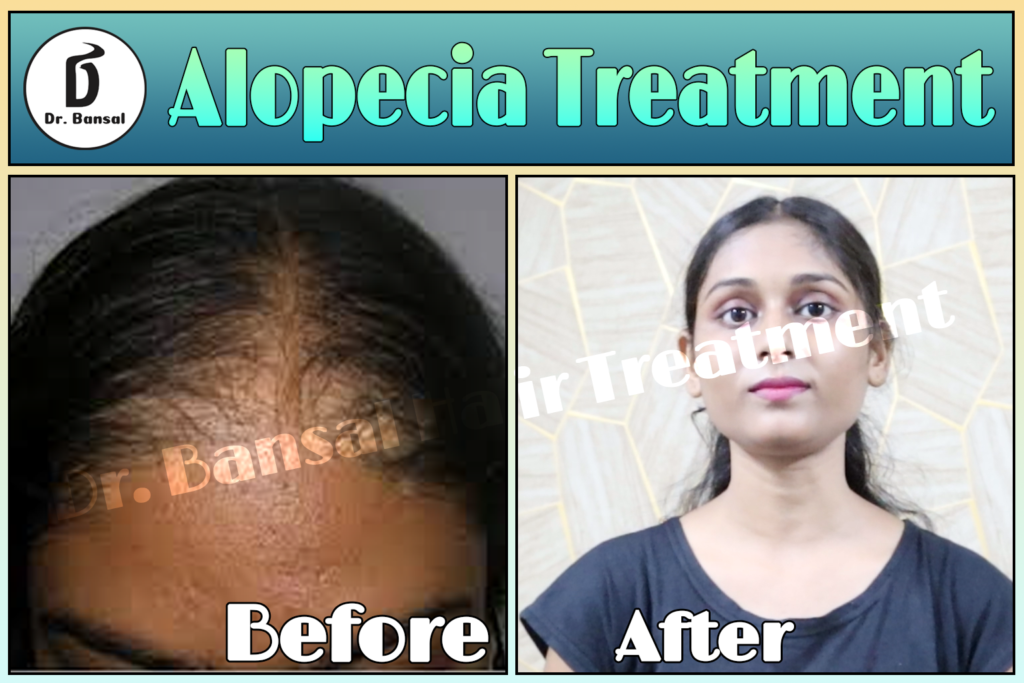
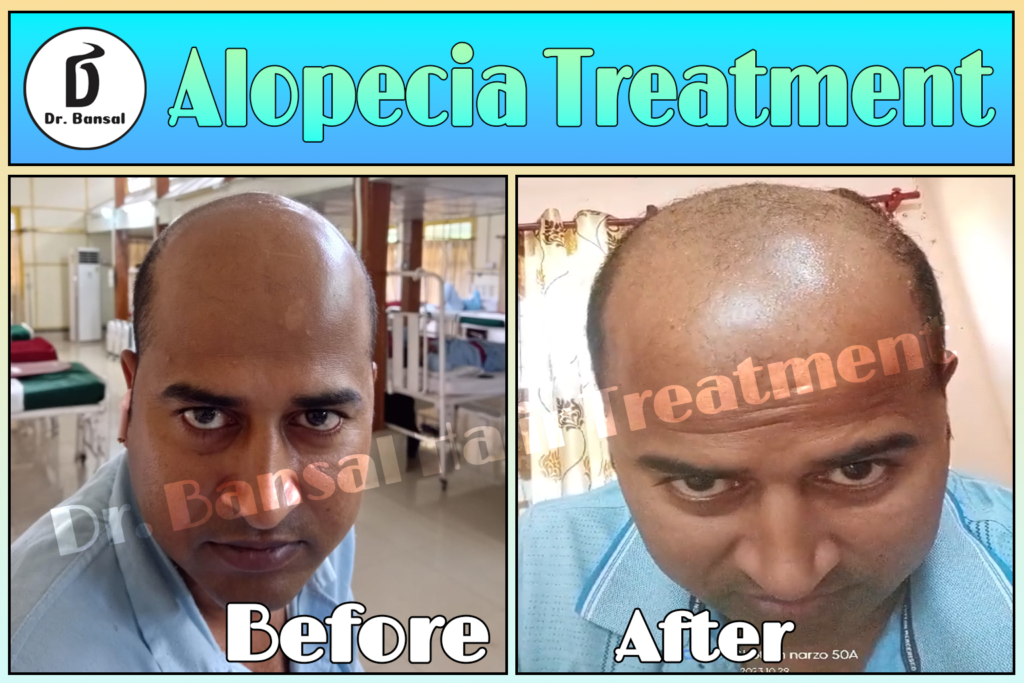
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition characterized by sudden, patchy hair loss. It affects millions worldwide, transcending age, gender, and ethnicity. Patchy Hair Loss This condition is not merely a cosmetic concern; it significantly impacts the psychological and emotional well-being of affected individuals. As a healthcare professional, it is crucial to comprehend the underlying mechanisms, clinical manifestations, prognosis, and treatment options available for alopecia areata. Patchy Hair Loss
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Pathophysiology
Alopecia areata is classified as an autoimmune disorder, wherein the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles. The exact cause remains uncertain, but genetic predisposition and environmental factors are believed to play crucial roles. Patchy Hair Loss In individuals with a genetic predisposition, various triggers — including stress, infections, and allergens — may activate the immune response, leading to inflammation around hair follicles. This inflammation halts the hair growth cycle, resulting in hair loss. Patchy Hair Loss
The role of cytokines, particularly interferons and interleukins, has been investigated, suggesting that they are involved in the hair follicle’s immune response. Recent studies also highlight the role of T lymphocytes, which infiltrate hair follicles and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in hair follicle cells. Patchy Hair Loss
Clinical Presentation
Alopecia areata commonly manifests as well-defined, round patches of hair loss on the scalp or other body areas. The following forms of alopecia areata are commonly recognized:
- **Alopecia Areata (Classic)**: Characterized by one or more patches of hair loss on the scalp or body.
- **Alopecia Totalis**: Involves total loss of hair on the scalp.
- **Alopecia Universalis**: This is the most severe form, resulting in total hair loss across the entire body.
- **Alopecia Areata Incognita**: An atypical variant, where hair loss occurs without noticeable patches. Instead, individuals may experience thinning hair or increased hair shedding. Patchy Hair Loss
Additional clinical signs may include:
– **Exclamation Mark Hairs**: Short, broken hairs at the margins of the bald patches. Patchy Hair Loss
– **Nail Changes**: Ridged, pitted, or white spots on the nails may be present in some patients.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of alopecia areata is primarily clinical. A thorough history and physical examination are essential. Key points include the pattern of hair loss, duration, family history of autoimmune diseases, and any preceding events that might trigger the condition, such as stress or infection. Patchy Hair Loss
In some cases, a **scalp biopsy** may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Histopathological examination typically reveals lymphocytic infiltration around hair follicles, consistent with an autoimmune phenomenon. **Trichoscopy**, a non-invasive technique utilizing a dermatoscope, can assist in identifying characteristic features of alopecia areata. Patchy Hair Loss
Prognosis
The prognosis of alopecia areata varies widely among individuals. Some may experience spontaneous regrowth, while others may face recurring episodes over the years. Factors influencing prognosis include:
– **Extent of Hair Loss**: Patients with limited patches often have a better prognosis than those with totalis or universalis forms.
– **Duration of Disease**: Chronic cases with prolonged hair loss may face a more challenging recovery. Patchy Hair Loss
– **Age of Onset**: Children and adolescents may demonstrate higher rates of spontaneous regrowth compared to adults.
– **Nail Involvement**: The presence of nail changes is generally associated with a poorer prognosis
Psychological Impact
The psychological ramifications of alopecia areata can be profound. Many affected individuals report increased feelings of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Social stigma surrounding hair loss may lead to withdrawal from social situations or adverse effects on personal relationships. Given these challenges, mental health support is crucial for individuals coping with alopecia areata. Patchy Hair Loss
Counseling and support groups can provide valuable resources, fostering a sense of community and shared experience. Encouraging open communication about the emotional impact of this condition is essential for promoting mental health and resilience. Patchy Hair Loss
Treatment Options
The management of alopecia areata aims not only to promote hair regrowth but also to address the underlying autoimmune process and the psychosocial impact of the condition. Various treatment modalities exist, each with its own efficacy profile:
- **Corticosteroids**: These are anti-inflammatory medications commonly used for alopecia areata. They can be administered via injections directly into bald patches or topically in the form of ointments. Systemic corticosteroids may be considered in severe cases.
- **Minoxidil**: This topical solution is used to stimulate hair growth. While it is more effective for androgenetic alopecia, some patients with alopecia areata report positive outcomes.
- **Anthralin**: A topical medication that alters immune response, anthralin can stimulate hair regrowth in some patients.
- **Contact Immunotherapy**: This technique involves applying a sensitizing agent (such as diphencyprone – DPCP) to induce an allergic reaction, prompting the immune system to redirect its focus. This approach may be particularly effective for extensive alopecia areata.
- **Biologic Agents**: Newer treatments targeting specific immune pathways, such as JAK inhibitors (e.g., tofacitinib and ruxolitinib), show promise in clinical trials. By modulating the immune response, these agents may facilitate hair regrowth in cases resistant to standard treatments.
- **Light Therapy**: Also known as phototherapy, ultraviolet light treatment can reduce inflammation in the scalp and may promote hair regrowth.
- **Supportive Therapies**: Psychological counseling, support groups, and stress management techniques are vital components of an integrative approach to treatment. Providing patients with coping strategies can alleviate some emotional burdens associated with hair loss.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Individuals coping with alopecia areata may find relief in complementary and alternative therapies. While the evidence supporting these approaches is variable, some individuals report benefits from:
– **Dietary Modifications**: A balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, D, E, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids can support hair health. However, there is no specific diet proven to improve alopecia areata.
– **Stress Management Techniques**: Since stress is a suspected trigger for alopecia areata, practices such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can be helpful.
– **Cosmetic Solutions**: Hairpieces, wigs, and cosmetic products can enhance self-esteem and provide a sense of normalcy in daily life.
Research and Future Directions
Research into the pathophysiology of alopecia areata is ongoing, focusing on the genetic, immunological, and environmental factors contributing to the condition. Advancements in treatment options are promising, particularly with the advent of targeted therapies such as JAK inhibitors, which have shown positive outcomes in clinical trials.
Additionally, ongoing investigations into the psychological impact of alopecia areata aim to develop comprehensive supportive care strategies that address both physical and emotional needs. Increased public awareness and education about alopecia areata can also help combat stigma and foster understanding and acceptance.
Conclusion
Alopecia areata is a multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive understanding from healthcare providers. While treatment options have expanded, the psychological aspects of the condition must not be overlooked. An integrative approach that combines medical intervention with psychological support can help individuals navigate the challenges of alopecia areata. Continued research and awareness are vital for improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
As healthcare providers, we must strive to remain empathetic and informed, fostering an environment of support for our patients dealing with alopecia areata, ultimately helping them regain their confidence and well-being.
**Note**: While this article is written in the style that a medical professional like Dr. Bansal might employ, it’s not an actual publication by any specific author. For clinical advice and treatment, individuals should consult qualified healthcare providers.

